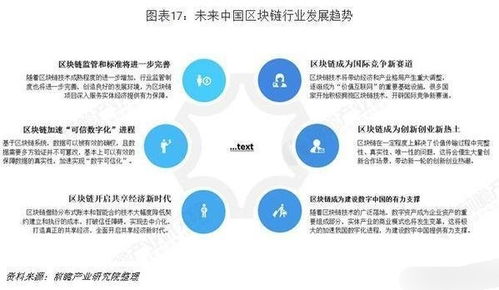
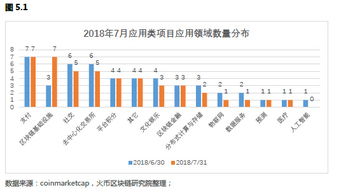
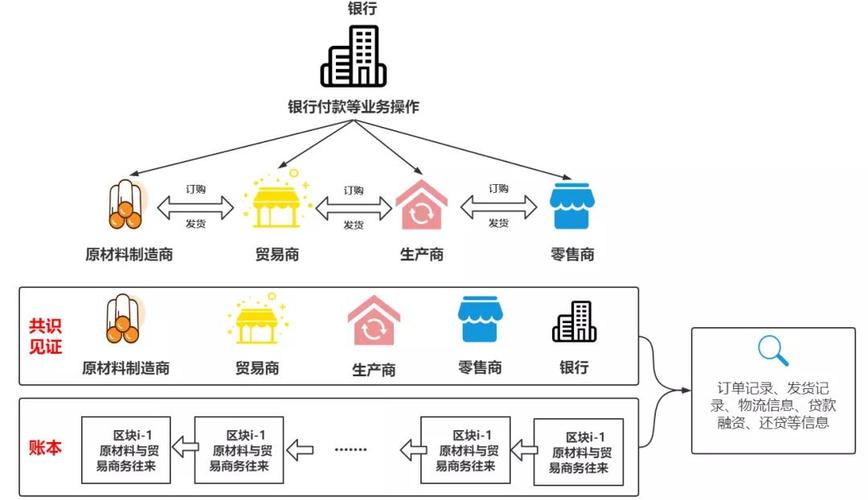
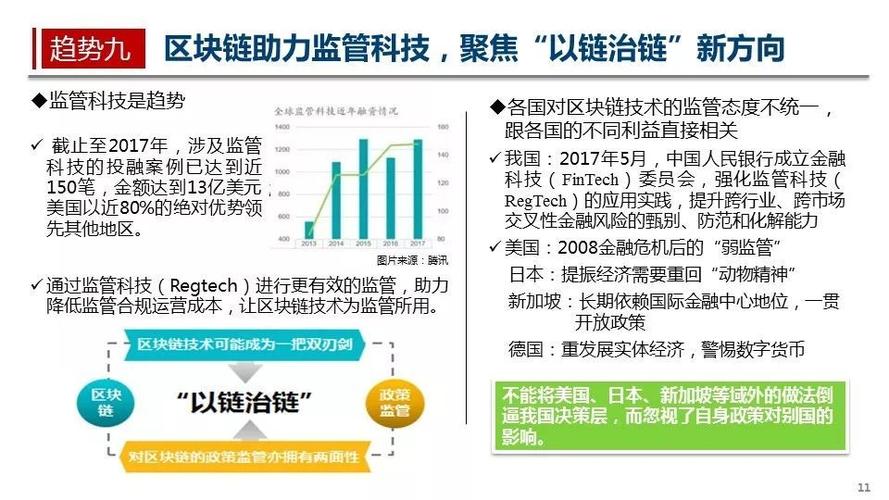
区块链在工程上的应用
Title: Blockchain Applications in Engineering

Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized and immutable nature, has been making significant strides across various industries, including engineering. Its ability to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency has led to innovative applications within the engineering sector. Let's delve into some key areas where blockchain is making an impact in engineering.
Supply Chain Management
One of the most prominent applications of blockchain in engineering is supply chain management. The complex and interconnected nature of supply chains in engineering projects often leads to challenges such as counterfeit parts, delays, and disputes. Blockchain provides a transparent and tamperproof ledger that enables stakeholders to track the journey of components and materials from their origin to the final assembly. By recording each transaction and movement on the blockchain, companies can ensure the authenticity and quality of materials while reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
Intellectual Property Protection
Innovation is the lifeblood of engineering, and protecting intellectual property (IP) rights is crucial for fostering creativity and investment. Blockchain offers a decentralized and secure platform for registering and managing IP rights, including patents, designs, and copyrights. Smart contracts, selfexecuting agreements coded on the blockchain, can automate the licensing and royalty distribution process, ensuring that creators are fairly compensated for their inventions and designs.
Project Management and Collaboration
Engineering projects often involve numerous stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and clients, collaborating across different locations and time zones. Blockchainbased project management platforms provide a single source of truth for project documentation, contracts, and communications. Smart contracts can automate payment schedules and milestone verification, reducing disputes and streamlining the project delivery process. Additionally, blockchain enhances data security and confidentiality, protecting sensitive project information from unauthorized access or tampering.
Asset Management and Maintenance
The maintenance of engineering assets, such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure, is critical for ensuring operational efficiency and safety. Blockchainpowered asset management systems enable realtime tracking of asset ownership, maintenance history, and performance data. By recording maintenance activities and sensor readings on the blockchain, engineers can proactively identify maintenance needs, optimize asset utilization, and extend the lifespan of equipment. Smart contracts can automate maintenance schedules and trigger alerts for servicing, reducing downtime and minimizing costly repairs.
Quality Assurance and Compliance
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and quality assurance requirements is paramount in engineering projects, especially in highly regulated sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. Blockchain facilitates the transparent and auditable recording of quality control processes, inspection results, and regulatory certifications. By digitizing compliance documents and audit trails on the blockchain, engineering firms can streamline the certification process, demonstrate regulatory compliance, and mitigate the risk of noncompliance penalties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology holds immense potential to transform the engineering industry by enhancing supply chain visibility, protecting intellectual property, streamlining project management, optimizing asset maintenance, and ensuring regulatory compliance. As blockchain adoption continues to grow, engineering firms that embrace this disruptive technology will gain a competitive edge in delivering innovative solutions and driving operational excellence. By harnessing the power of blockchain, the engineering sector can embark on a new era of transparency, efficiency, and collaboration.