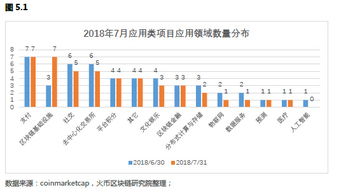
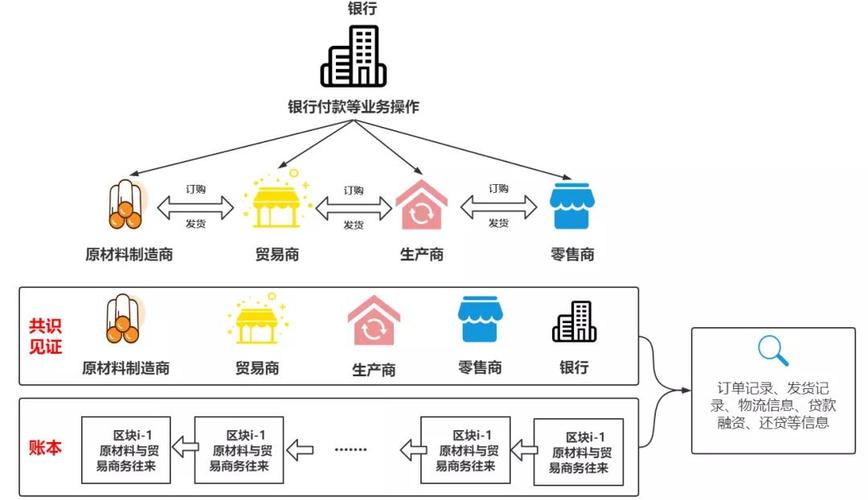
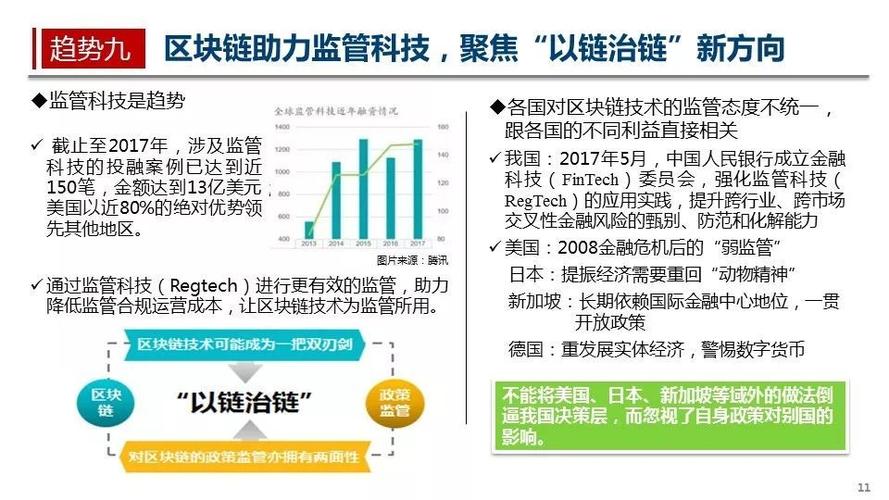
区块链的简单表达是什么
Title: Understanding Blockchain: A Simplified Explanation
Introduction:
Blockchain, often described as a revolutionary technology, has gained immense popularity in recent years. Originating from the world of cryptocurrencies, blockchain has become a versatile tool with applications across various industries. In this article, we will provide a simplified explanation of blockchain, its key principles, and its potential benefits.
1. What is Blockchain?
Blockchain can be thought of as a digital ledger that records transactions and stores them across multiple computers or nodes. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized peertopeer network, making it transparent, secure, and tamperresistant.
2. Basic Components of Blockchain:
a. Blocks: Each transaction is grouped into blocks, which contain a unique identifier called a hash. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain.
b. Nodes: Computers within the network that store and verify transactions. Every node has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring redundancy and data integrity.
c. Consensus Mechanism: A method through which nodes agree on the validity of transactions. Blockchain typically employs mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
3. Key Principles of Blockchain:
a. Decentralization: No central authority governs the network, ensuring that no single entity can control or manipulate the data.
b. Transparency: All transactions recorded on the blockchain are visible to every participant, enhancing trust and accountability.
c. Security: Transactions are encrypted using cryptographic algorithms. As data is distributed across the network, it becomes incredibly difficult for hackers to alter or compromise the information.
d. Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be erased or modified, ensuring a permanent and auditable record.
4. Potential Benefits of Blockchain:
a. Enhanced Security: Blockchain's cryptographic algorithms and decentralized structure provide a high level of security, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
b. Increased Efficiency: Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and streamlines administrative processes, reducing time and costs associated with thirdparty verification.
c. Trust and Transparency: As every participant has access to the same information, blockchain promotes trust and transparency in complex networks where multiple parties are involved.
d. Traceability: Blockchain's immutable nature allows for the tracking of assets or products throughout their lifecycle. This capability is particularly useful in supply chain management, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeiting.
e. Smart Contracts: Blockchain can execute programmable contracts known as smart contracts, which automatically enforce predefined conditions, reducing reliance on intermediaries and minimizing the potential for human error.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology holds tremendous potential to revolutionize numerous industries by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions. As the technology continues to evolve, its adoption and implementation will likely become more widespread. Whether it is financial services, healthcare, supply chain, or government sectors, understanding blockchain's principles and potential benefits can be instrumental in leveraging its advantages and driving future innovation.