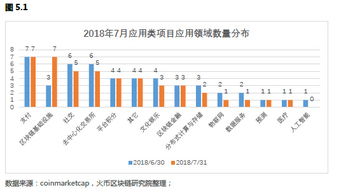
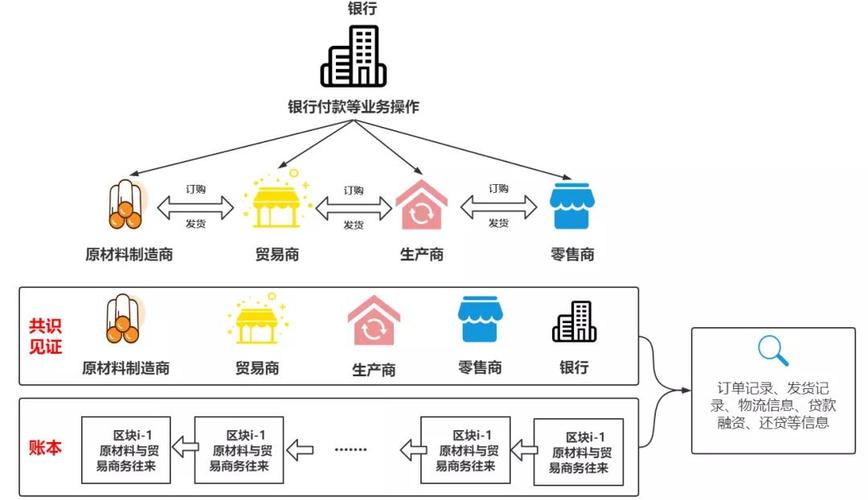
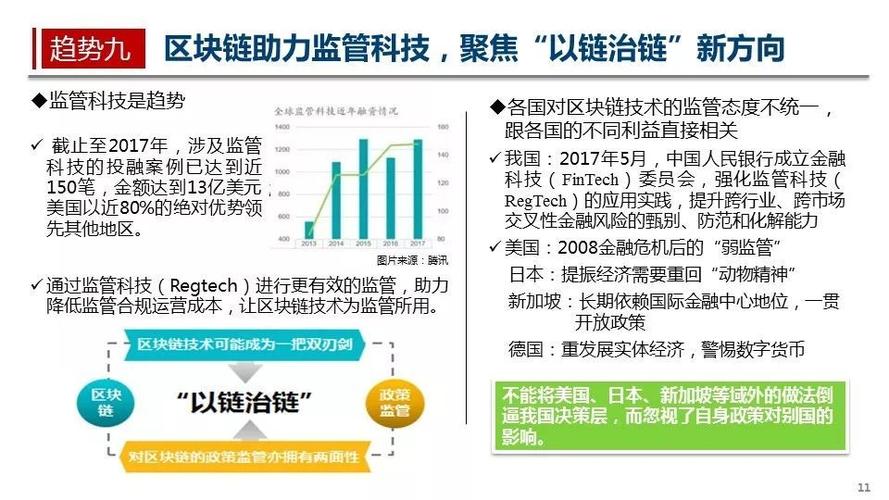
区块链有效的隐私保护
Title: Deciphering Private Blockchain Networks with Images
In the realm of blockchain technology, private blockchains represent a fascinating domain with distinct characteristics and functionalities. Understanding private blockchains, particularly through visual aids, can elucidate their intricacies and applications.
A private blockchain, also known as a permissioned blockchain, is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) where access and permissions to participate in the network are restricted to a specific group of participants. Unlike public blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, where anyone can join the network and participate in the consensus process, private blockchains are operated by a designated set of nodes controlled by a single organization or consortium.
Private blockchains exhibit several features that differentiate them from public blockchains:
- Access Control: Participants in a private blockchain network are known and identified, and access to the network is restricted.
- Permissioned Participation: Only authorized nodes can participate in the consensus mechanism and perform various operations on the blockchain.
- Centralized Governance: Private blockchains are typically governed by a central entity or consortium, allowing for greater control over the network.
- Enhanced Privacy: Transactions and data within a private blockchain are often encrypted or made visible only to authorized parties, ensuring confidentiality.
Let's delve into the components of a private blockchain network through a visual representation:

Private blockchains find applications across various industries where privacy, scalability, and control are paramount:
- Financial Services: Private blockchains can streamline interbank transactions, trade finance, and settlements while ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking and tracing products, verifying authenticity, and enhancing transparency in supply chains.
- Healthcare: Securing patient records, facilitating interoperability among healthcare providers, and managing pharmaceutical supply chains.
- Government: Improving transparency, efficiency, and security in public services such as identity management, voting systems, and land registries.
Private blockchains offer a compelling alternative to public blockchains, catering to specific use cases where controlled access, scalability, and privacy are essential. Through visual representations and comprehensive understanding, organizations can harness the power of private blockchains to drive innovation and transformation across industries.