Title: Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Technology: Decentralized Ledger System
Blockchain, in its essence, is a decentralized ledger system. It functions as a distributed database that records transactions across a network of computers in a manner that ensures security, transparency, and immutability. Each record, or "block," in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This structure creates a secure and transparent record of transactions that cannot be easily altered or tampered with.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates on a peertopeer network of computers, often referred to as nodes. These nodes work together to validate and record transactions in a chronological order, forming a chain of blocks. When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcasted to the network and grouped with other transactions into a block.
Before being added to the blockchain, the validity of the transactions within the block is verified by the nodes through a process called consensus. This process ensures that all copies of the blockchain across the network are synchronized and consistent.
Once a block is validated and added to the blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of the ledger. Any attempts to alter the data within a block would require the alteration of all subsequent blocks in the chain, making it nearly impossible to tamper with the information stored on the blockchain.
Key Features of Blockchain
1.
Decentralization
: Unlike traditional centralized systems where data is stored on a single server controlled by a central authority, blockchain operates on a decentralized network where data is distributed across multiple nodes. This decentralization eliminates the need for a central authority, making the system more resilient to failures and attacks.2.
Transparency
: All transactions recorded on the blockchain are visible to all participants in the network. This transparency fosters trust among users and ensures accountability.3.
Immutability
: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity and reliability of the data stored on the blockchain.4.
Security
: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and prevent unauthorized access. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous block, forming a secure chain that is resistant to tampering.Applications of Blockchain
1.
Cryptocurrencies
: The most wellknown application of blockchain is in the creation and management of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain serves as the underlying technology that enables secure and transparent transactions of digital assets.2.
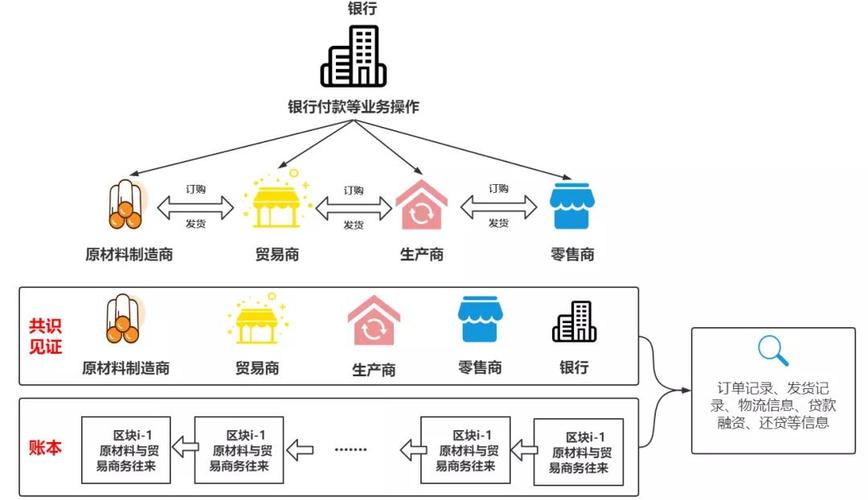
Supply Chain Management
: Blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods across a supply chain, providing transparency and traceability. This can help streamline processes, reduce fraud, and ensure the authenticity of products.3.
Smart Contracts
: Blockchain enables the creation of smart contracts, which are selfexecuting contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute and enforce themselves when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
4.
Identity Management
: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized identity management systems, giving individuals more control over their personal data and reducing the risk of identity theft.Challenges and Future Outlook
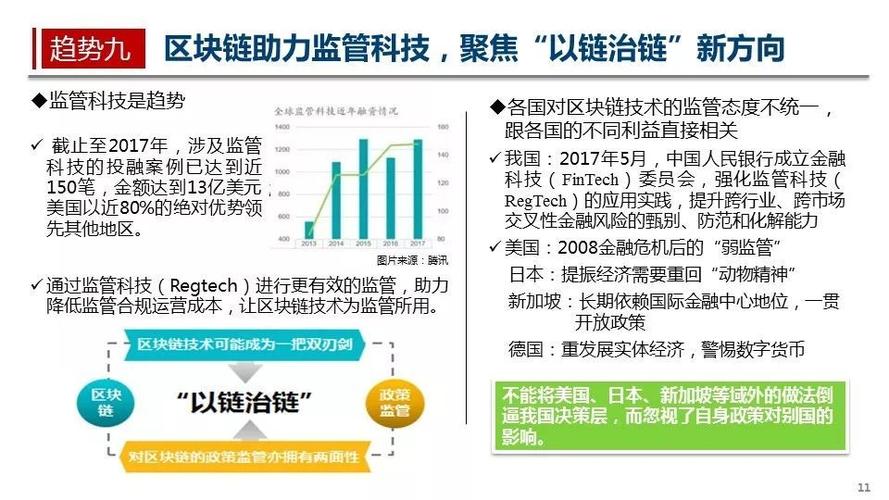
While blockchain technology holds immense promise, it also faces several challenges, including scalability, interoperability, and regulatory concerns. As the technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial to realizing its full potential.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for blockchain remains optimistic. As businesses and industries increasingly recognize the value of decentralization, transparency, and security, blockchain is poised to revolutionize various sectors, from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and beyond.
In conclusion, blockchain technology represents a fundamental shift in how data is stored, shared, and managed. By leveraging decentralization, transparency, and immutability, blockchain has the potential to transform numerous industries and redefine the way we interact with digital information.