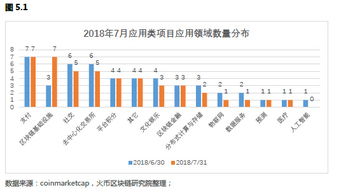
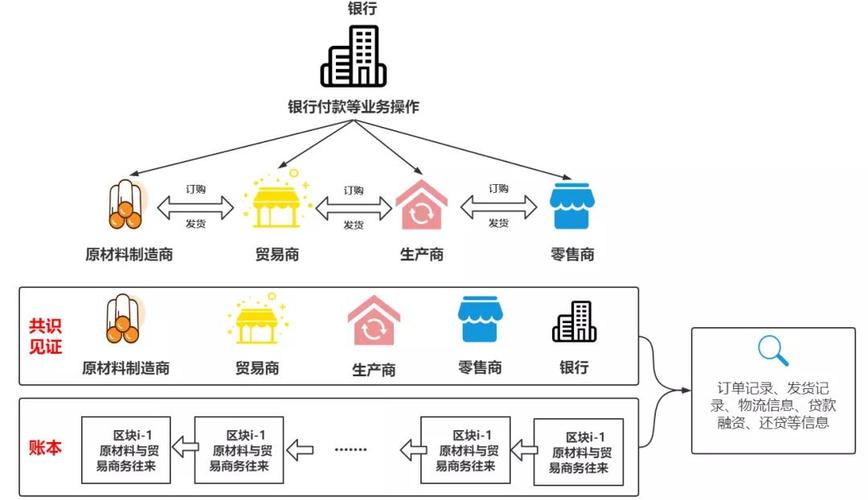
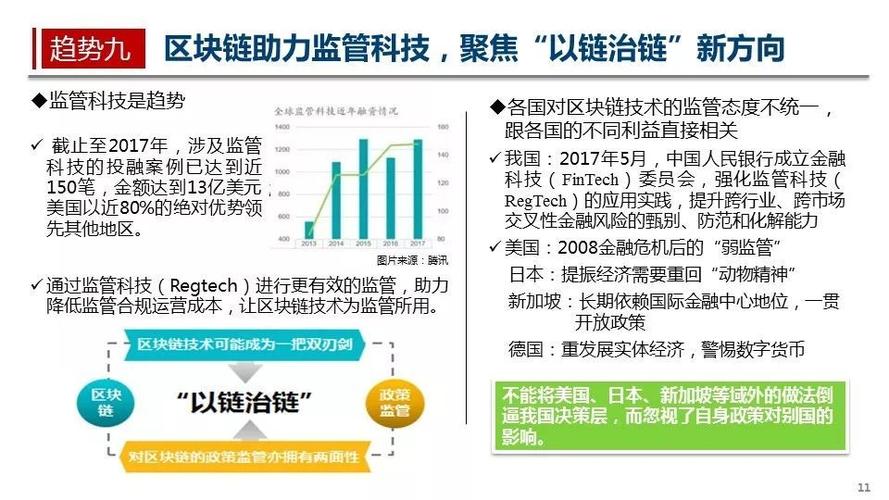
区块链英文简称
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries, offering decentralized and secure solutions for a myriad of applications. In this essay, we will delve into the fundamentals of blockchain technology, its key features, and its potential impact on the future.
Introduction to Blockchain
At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is stored in a "block," which is then linked to the previous block, forming a chain. This chain of blocks creates an immutable record of transactions, ensuring transparency and security.
Key Features of Blockchain
1.
Decentralization:
Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or governments, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
2.
Transparency:
Every transaction on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network. This transparency fosters trust among users and ensures the integrity of the system.3.
Immutability:
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature prevents fraud and tampering, enhancing the reliability of the data.4.
Security:
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect the integrity of the network. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous block, making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to alter the data.Applications of Blockchain
1.
Cryptocurrencies:
The most wellknown application of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies enable peertopeer transactions without the need for intermediaries.2.
Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain technology can be used to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain. By recording each transaction on the blockchain, companies can verify the authenticity and origin of products, reducing counterfeiting and improving transparency.3.
Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts are selfexecuting contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce the terms when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining processes.4.
Identity Management:
Blockchain technology can provide a secure and decentralized solution for identity management. By storing identity information on the blockchain, individuals can have greater control over their personal data and reduce the risk of identity theft.Challenges and Future Outlook
While blockchain technology holds immense potential, it also faces several challenges, including scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and energy consumption. However, as the technology continues to evolve and mature, these challenges are being addressed, paving the way for widespread adoption across industries.
In conclusion, blockchain technology offers a decentralized, transparent, and secure solution for a wide range of applications. By harnessing the power of blockchain, businesses and organizations can streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance trust among users. As we look to the future, the potential impact of blockchain technology is boundless, reshaping industries and driving innovation on a global scale.
I provided a comprehensive introduction to blockchain technology, covering its key features, applications, challenges, and future outlook. If you need more details on any specific aspect or have any other questions, feel free to ask!